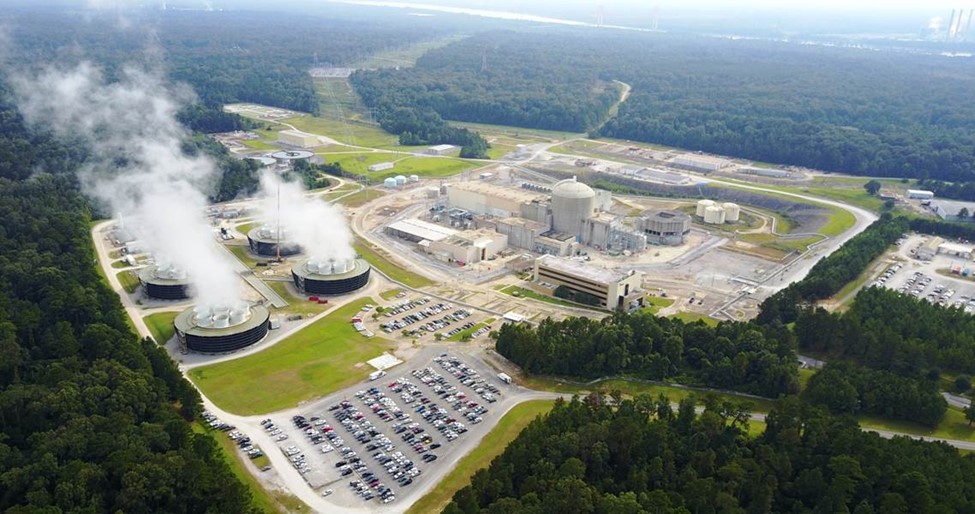
Entergy’s River Bend in St. Francisville, La., a boiling water reactor and one of five Entergy nuclear power reactors. (Photo: Entergy)
The Department of Energy’s Gateway for Accelerated Innovation in Nuclear (GAIN) announced June 20 that two companies—one power plant operator and one advanced reactor developer—are getting vouchers to access the extensive nuclear research capabilities and expertise available across the DOE national laboratories in the third round of GAIN vouchers awarded for fiscal year 2024.
Representatives of Terrestrial Energy and Schneider Electric at the MOU signing ceremony. (Source: Terrestrial Energy)
Terrestrial Energy and Schneider Electric are teaming to deploy Terrestrial Energy's integral molten salt reactor (IMSR) to provide zero-emission power to industrial facilities and large data centers.
The companies signed a memorandum of understanding in April to jointly develop commercial opportunities with high-energy users looking for reliable, affordable, and zero-carbon baseload supply. Terrestrial Energy said that working with Schneider “offers solutions to the major energy challenges faced by data center operators and many heavy industries operating a wide range of industrial processes such as hydrogen, ammonia, aluminum, and steel production.”
An aerial view of Westinghouse’s Springfields Fuel Fabrication Facility, near Preston, Lancashire, in northwestern England. (Photo: Westinghouse)
Through its now one-year-old Nuclear Fuel Fund, the U.K. government has awarded Westinghouse three grants to upgrade and expand the Springfields Fuel Fabrication Facility to support Britain’s next-generation nuclear reactors, the American-based company announced yesterday.
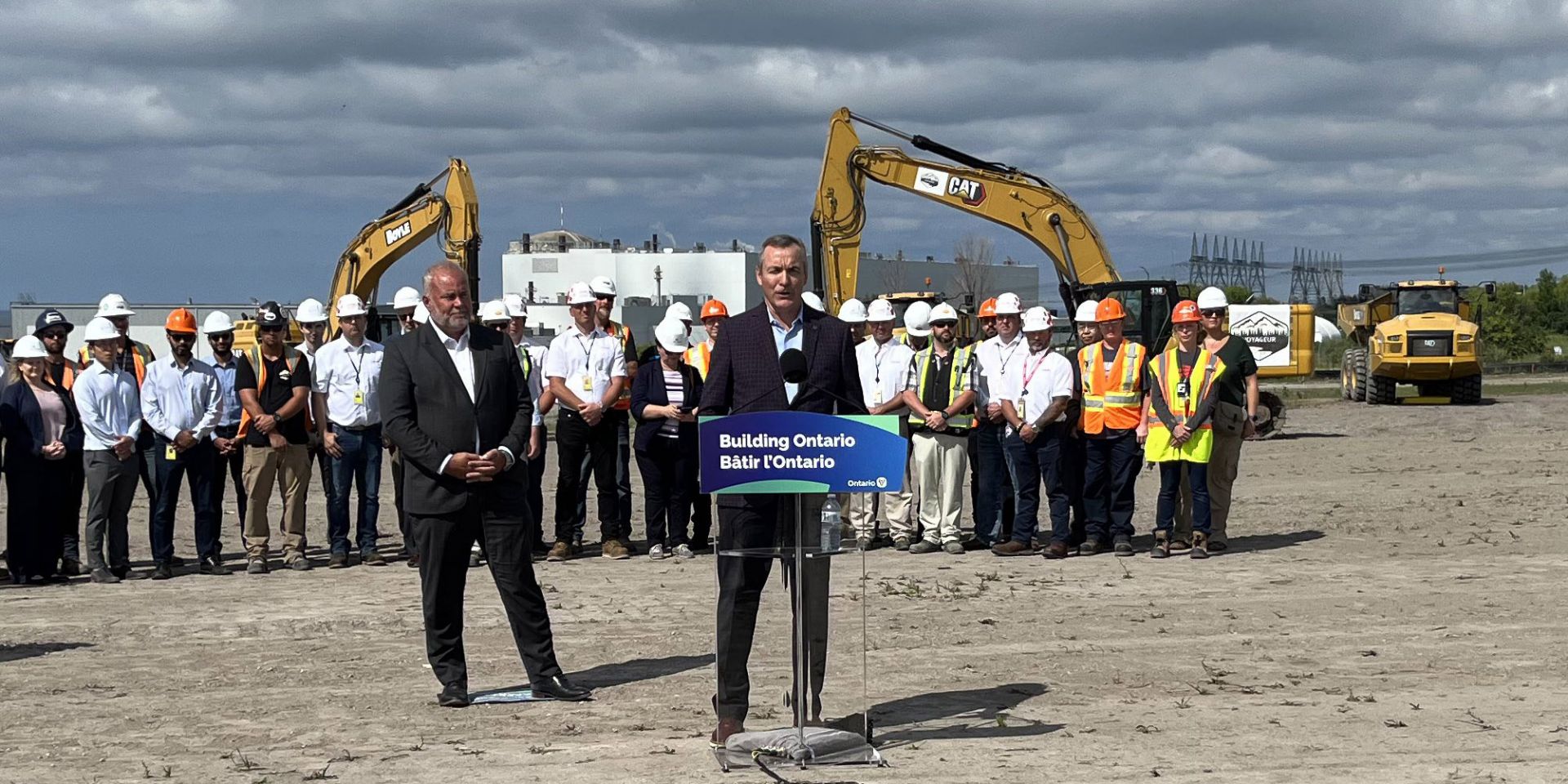
Ontario energy minister Todd Smith (left) and Ontario Power Generation president and CEO Ken Hartwick announce plans for three more BWRX-300 units at Darlington. (Photo: OPG)
If we’re in a new nuclear renaissance, its capital would appear to be Ontario. On July 7, just two days after debuting a collaboration with Bruce Power to build up to 4.8 GW of new nuclear generation at the Bruce plant, the government of Ontario announced that it is working with Ontario Power Generation to begin planning and licensing for the deployment of three additional GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy (GEH) BWRX-300 small modular reactors at that utility’s Darlington site.
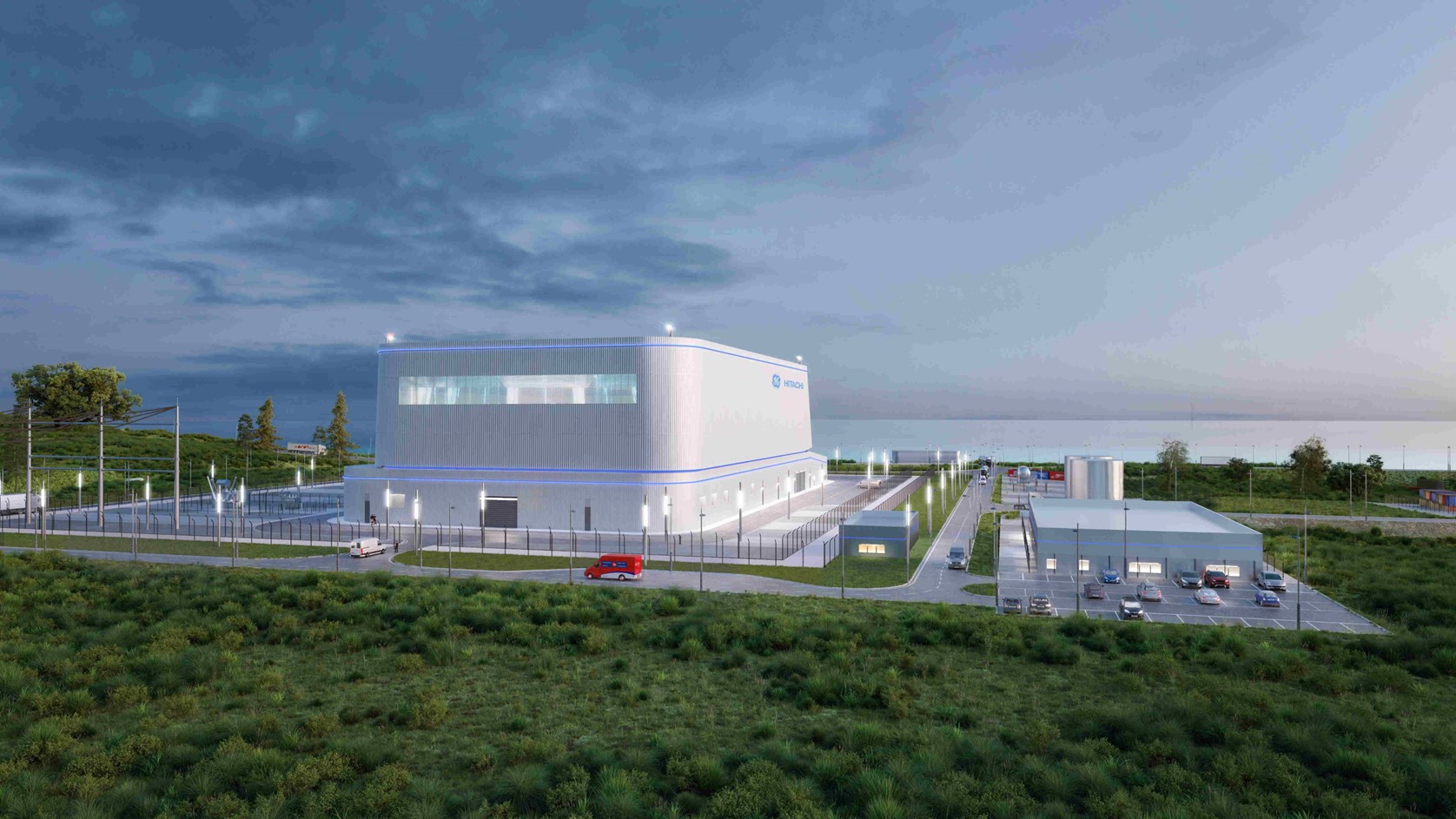
An illustration of an IMSR plant. (Image: Terrestrial Energy)
Ontario–based Terrestrial Energy announced yesterday that its U.S. branch has been awarded a regulatory assistance grant from the Department of Energy to support the company’s Nuclear Regulatory Commission licensing program for the Integral Molten Salt Reactor (IMSR) plant.
A rendition of Terrestrial Energy’s IMSR. (Image: NRC)
The Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission (CNSC) has completed phase two of its prelicensing vendor design review for Terrestrial Energy’s Integral Molten Salt Reactor (IMSR), the Ontario-based advanced nuclear technology firm announced Tuesday. Phase one of the VDR commenced in April 2016 and was completed in November of the following year.
A rendering of the BWRX-300 small modular reactor. (Image: GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy)
Wilmington, N.C.–based GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy and Canadian firms Ontario Power Generation, SNC-Lavalin, and Aecon announced this morning the signing of a contract for the deployment of a BWRX-300 small modular reactor at OPG’s Darlington nuclear site in Canada. According to the announcement, it is the first commercial contract for a grid-scale SMR in North America.
Representatives of OPG and GEH join Ontario government officials on December 2 to mark the start of site preparations for the Darlington SMR project. (Photo: Doug Ford via Twitter)
The Ontario government has announced the start of site preparation at the Darlington nuclear power plant for Canada’s first grid-scale small modular reactor: GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy’s (GEH) BWRX-300.
Artist’s rendering of a BWRX-300 plant. (Image: GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy)
Canada Infrastructure Bank (CIB) has finalized an agreement with Ontario Power Generation, committing C$970 million (about $715 million) to Canada’s first small modular reactor, to be located at OPG’s Darlington nuclear power plant in Clarington, Ontario.
A state-owned enterprise founded in 2017, CIB is charged with financially supporting revenue-generating infrastructure projects in the public interest via public-private partnerships. The agreement with OPG is the bank’s largest investment in clean power to date, according to a Tuesday joint announcement.
The Estonian flag. (Image: WikiCommons)
Moving forward with its plan for small modular reactor deployment in Estonia, Fermi Energia has issued tenders to three SMR firms—GE Hitachi (GEH), NuScale Power, and Rolls-Royce, developers of the BWRX-300, NuScale Power Module, and Rolls-Royce SMR, respectively.
Artistic rendering of a NuScale nuclear power plant. (Image: NuScale Power)
NuScale Power yesterday announced the signing of a memorandum of understanding with Estonia’s Fermi Energia, a company focused on small modular reactor development to address the Baltic state’s climate and energy security goals.
Under the MOU, Fermi Energia will evaluate the Portland, Ore. – based firm’s small modular reactor design for deployment in Estonia. (There are no nuclear power facilities in Estonia or in the other Baltic countries, Latvia and Lithuania.)
Artist’s rendering of the IMSR Core-Unit. (Credit: Terrestrial Energy)
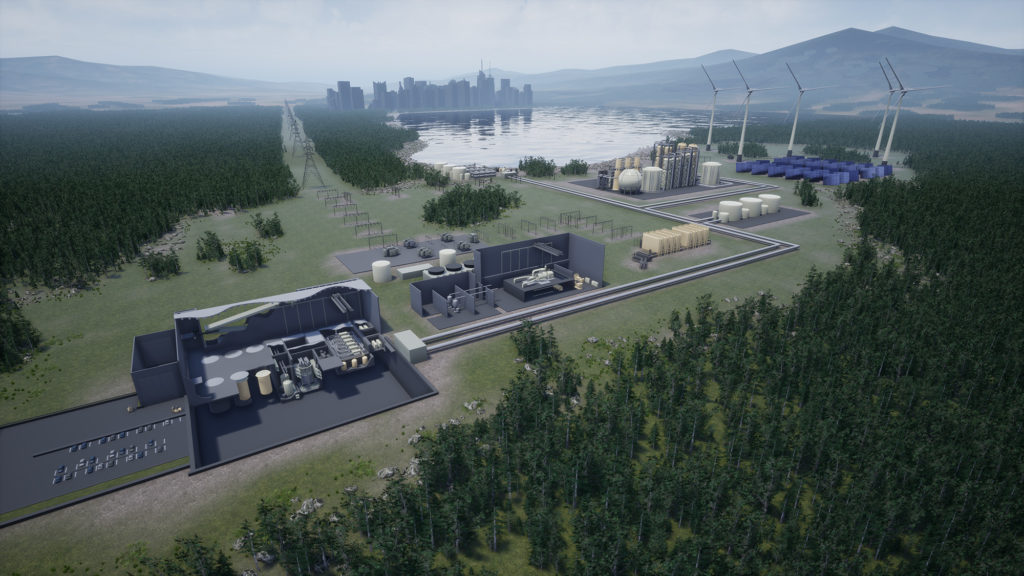
In the ongoing quest to mitigate the effects of climate change, new technology can create new solutions. Even today, however, coal is still a main source of power around the globe, often out of necessity. Many coal-burning plants have already been converted for gas or biomass, but these measures alone are not nearly enough to meet net-zero carbon goals. There is a better solution, however: repowering coal plants with nuclear technology—specifically, Generation IV reactors.
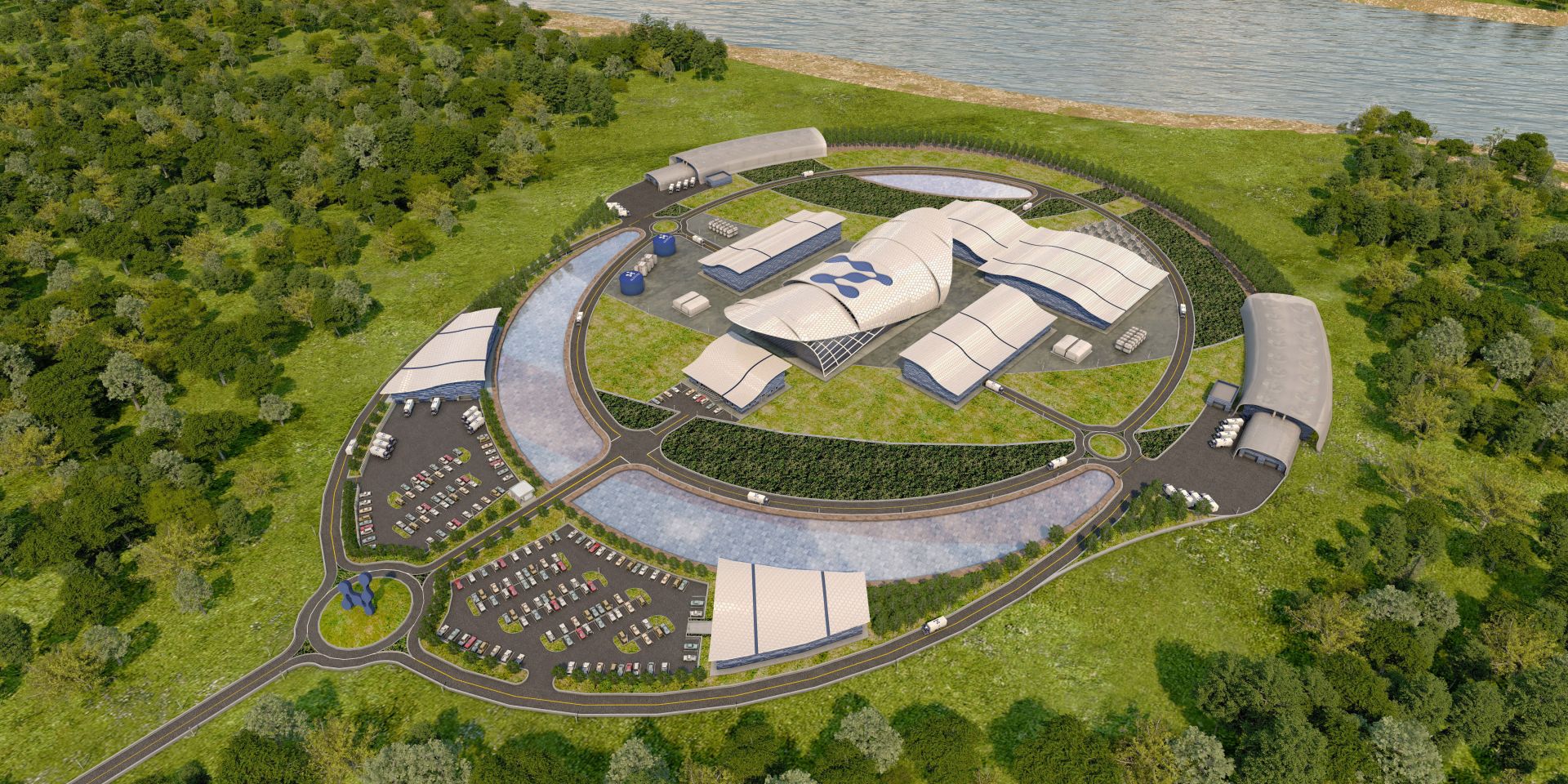
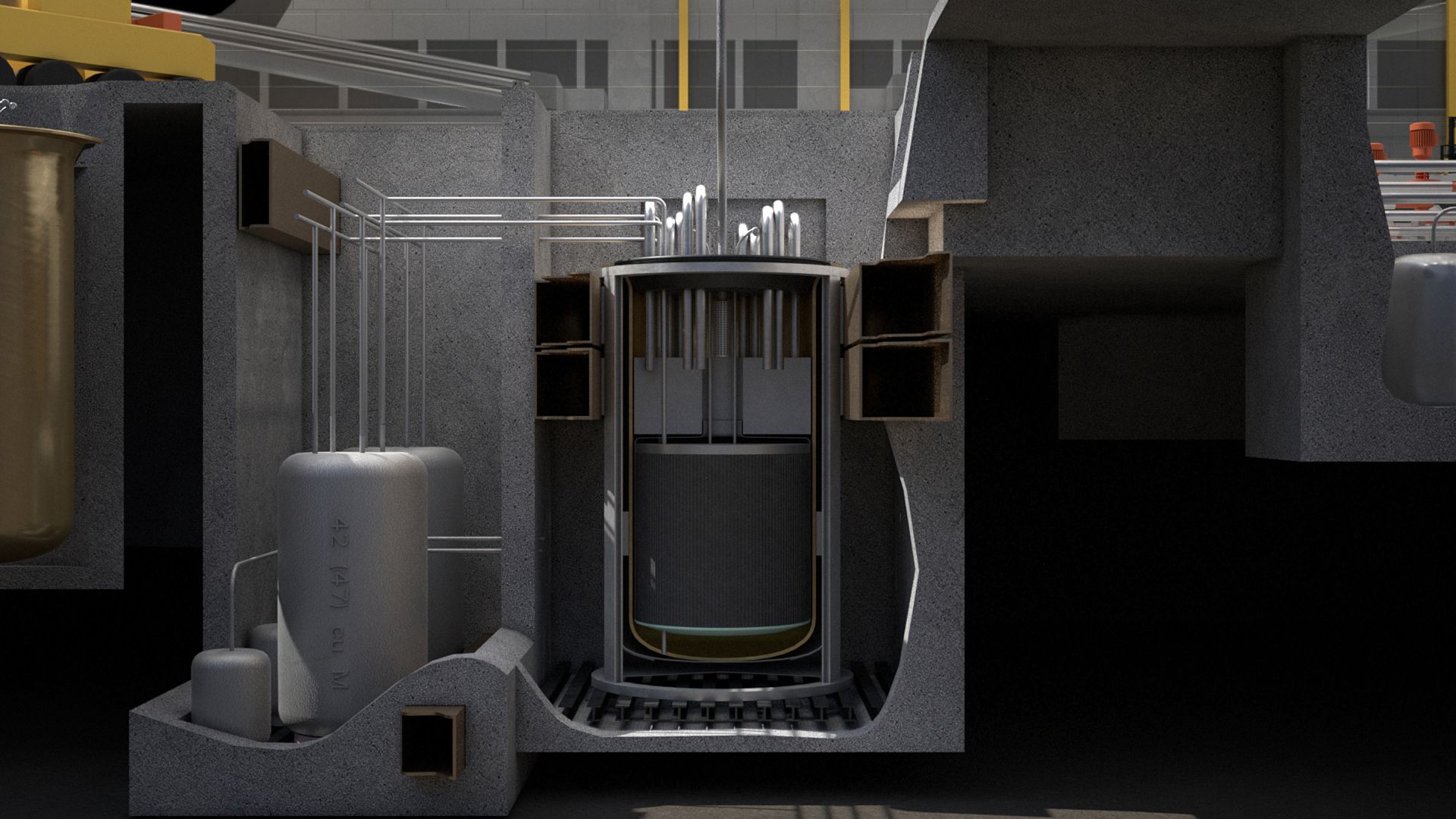
A cutaway of the Integral Molten Salt Reactor and balance of plant. (Image: Terrestrial Energy)
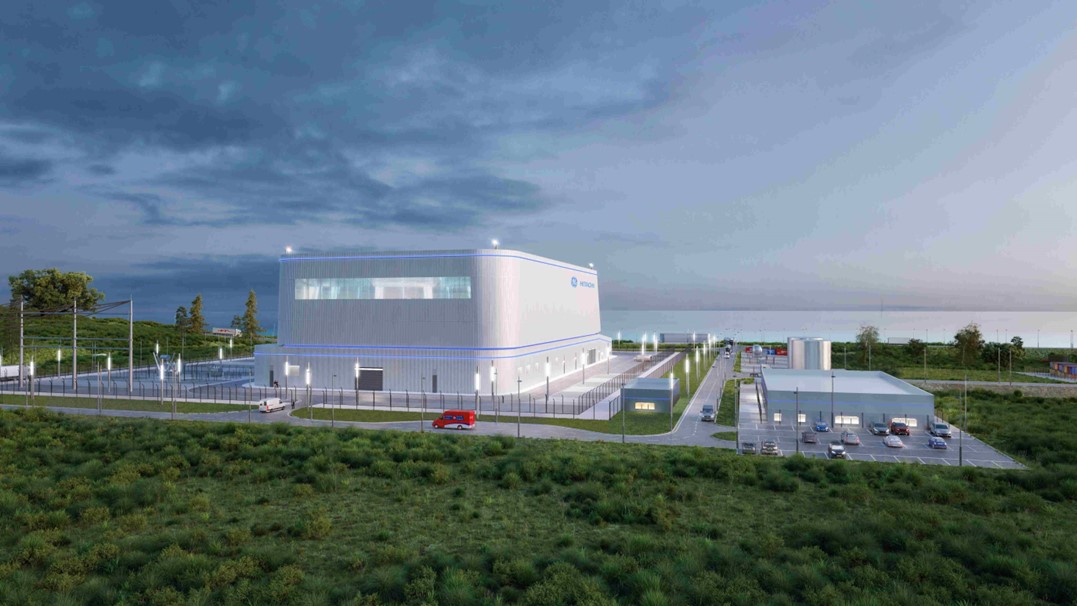
Ammonia is a carbon-free energy carrier that could be produced using thermal energy from nuclear power plants. Terrestrial Energy announced June 9 that it has signed an agreement with engineering firm KBR to explore the use of its Integral Molten Salt Reactor (IMSR) for both hydrogen and ammonia production.
Computer rendering of an IMSR400 plant. (Image: Terrestrial Energy)
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission and Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission have completed a first joint technical review of Terrestrial Energy’s Integral Molten Salt Reactor, the company announced earlier this week.
The IMSR was selected in December 2019 to be the first advanced non–light water nuclear reactor technology to be studied under an August 2019 NRC/CNSC memorandum of cooperation aimed at enhancing regulatory effectiveness through collaborative work on technical reviews of advanced reactor and small modular reactor technologies.